上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
Screen Quest 活细胞cAMP检测价格 19177
产品规格
产品货号
| Ex (nm) | – | Em (nm) | – |
| 分子量 | – | 溶剂 | – |
| 存储条件 | – |
产品基本信息
产品名称:Screen Quest 活细胞cAMP检测
产品介绍
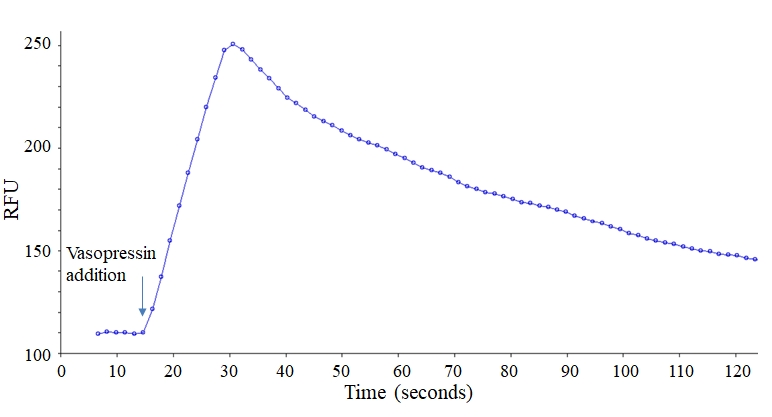
G蛋白偶联受体(GPCR)是药物发现计划中大的靶向受体之一。钙通量(通过Gq途径耦合)分析是筛选GPCR靶点的方法。然而,超过60%的已知GPCRs信号通过腺苷酸环化酶活性偶联到cAMP。现有的cAMP检测方法不仅需要细胞裂解,而且缺乏时间和空间分辨率。Screen Quest 活细胞cAMP检测以高通量的形式提供细胞内cAMP变化的实时监测,无需细胞裂解步骤。该方法通过含有外源性环核苷酸门控通道(CNGC)或混杂G蛋白Gα16的细胞系进行。该通道被细胞内cAMP水平升高,导致离子通量和细胞膜去极化,可通过荧光钙(如Calbryte 520 AM、Cal-520 AM、Fluo-8 AM或Fluo-4 AM和相应的免洗钙试剂盒)或荧光膜电位染料检测到。Gα16与特异性非Gq偶联受体的共表达将在受体刺激下产生细胞内钙信号。Screen Quest 活细胞cAMP检测提供细胞系和试剂,用于使用FLIPR、FDSS或其他等效的荧光酶标仪检测细胞内cAMP的变化。它已成功地用于测定Gs和Gi偶联GPCR活性。金畔生物是AAT Bioquest的中国代理商,为您提供优质的Screen Quest 活细胞cAMP检测。
适用仪器
| 荧光酶标仪 | |
| Ex: | 490nm |
| Em: | 525nm |
| cutoff: | 515nm |
| 推荐孔板: | 黑色透明底板 |
| 读取模式: | 底读模式/分液处理 |
图示
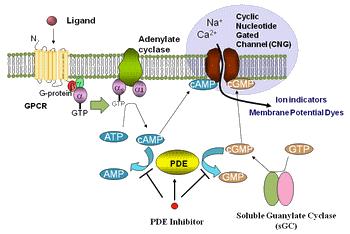 图1. Screen Quest 活细胞cAMP测定原理 |
参考文献
A cardiac mitochondrial cAMP signaling pathway regulates calcium accumulation, permeability transition and cell death
Authors: Wang Z, Liu D, Varin A, Nicolas V, Courilleau D, Mateo P, Caubere C, Rouet P, Gomez AM, V and ecasteele G, Fischmeister R, Brenner C.
Journal: Cell Death Dis (2016): e2198
Activation of P2X7 and P2Y11 purinergic receptors inhibits migration and normalizes tumor-derived endothelial cells via cAMP signaling
Authors: Avanzato, D and Genova, T and Pla, A Fiorio and Bernardini, M and Bianco, S and Bussolati, B and Mancardi, D and Giraudo, E and Maione, F and Cassoni, P and others
Journal: Scientific Reports (2016)
Changes in the Arabidopsis thaliana Proteome Implicate cAMP in Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses and Changes in Energy Metabolism
Authors: Alqurashi M, Gehring C, Marondedze C.
Journal: Int J Mol Sci (2016): 852
Odor-induced cAMP production in Drosophila melanogaster olfactory sensory neurons
Authors: Miazzi F, Hansson BS, Wicher D.
Journal: J Exp Biol (2016): 1798
Role of the cAMP Pathway in Glucose and Lipid Metabolism
Authors: Ravnskjaer K, Madiraju A, Montminy M.
Journal: Handb Exp Pharmacol (2016): 29
The pleiotropic role of exchange protein directly activated by cAMP 1 (EPAC1) in cancer: implications for therapeutic intervention
Authors: Almahariq M, Mei FC, Cheng X.
Journal: Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) (2016): 75
cAMP-Induced Histones H3 Dephosphorylation Is Independent of PKA and MAP Kinase Activations and Correlates With mTOR Inactivation
Authors: Rodriguez P, Rojas J.
Journal: J Cell Biochem (2016): 741
A cAMP Biosensor-Based High-Throughput Screening Assay for Identification of Gs-Coupled GPCR Ligands and Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors
Authors: Vedel L, Brauner-Osborne H, Mathiesen JM.
Journal: J Biomol Screen (2015): 849
Cardiac Hypertrophy Is Inhibited by a Local Pool of cAMP Regulated by Phosphodiesterase 2
Authors: Zoccarato A, Surdo NC, Aronsen JM, Fields LA, Mancuso L, Dodoni G, Stangherlin A, Livie C, Jiang H, Sin YY, Gesellchen F, Terrin A, Baillie GS, Nicklin SA, Graham D, Szabo-Fresnais N, Krall J, V and eput F, Movsesian M, Furlan L, Corsetti V, Hamilton G, Lefkimmiatis K, Sjaastad I, Zaccolo M.
Journal: Circ Res (2015): 707
Cardiac cAMP: production, hydrolysis, modulation and detection
Authors: Boularan C, Gales C.
Journal: Front Pharmacol (2015): 203
