上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
Cell Meter 荧光法细胞周期检测试剂盒 405nm激发 价格 2823
产品规格
产品货号
| Ex (nm) | 401 | Em (nm) | 460 |
| 分子量 | – | 溶剂 | – |
| 存储条件 | – |
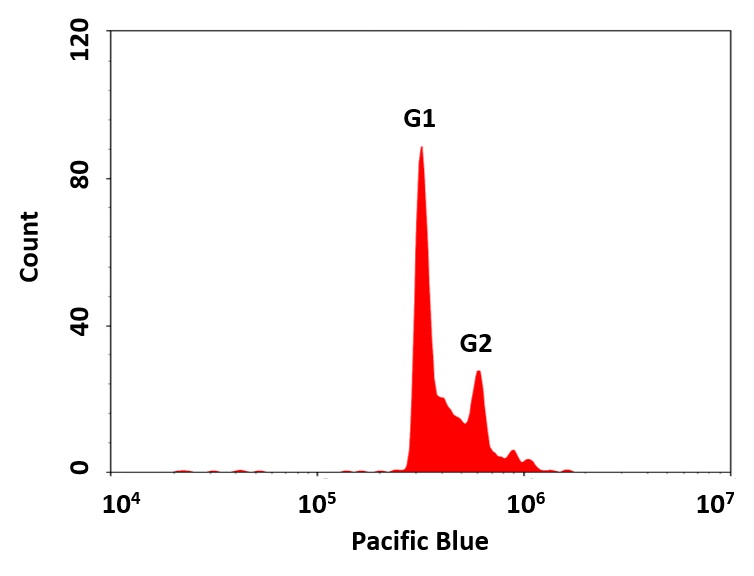
细胞周期具有四个连续阶段:G0 / G1,S,G2和M。在细胞通过细胞周期的过程中,其DNA在S(合成)阶段复制,并在M(有丝分裂)阶段在两个子细胞之间平均分配。这两个阶段由两个间隙阶段分开:G0 / G1和G2。这两个间隙相为细胞提供了生长时间,并使它们的蛋白质和细胞器的质量增加了一倍。在进入下一阶段的细胞周期之前,细胞还将它们用于检测内部和外部条件。细胞通过细胞周期的传递受到许多不同调节蛋白的控制。该特定试剂盒旨在通过在活细胞中使用我们专有的Nuclear Violet 检测细胞周期的进程和增殖。可以通过流式细胞术确定给定样品中处于G0 / G1,S和G2 / M期的细胞以及亚G1期处于凋亡之前的细胞的百分比。可以用流式细胞仪(PacificBlue®通道)检测用Nuclear Violet 染色的细胞。金畔生物是AAT Bioquest的中国代理商,为您提供优质的Cell Meter 荧光法细胞周期检测试剂盒。
点击查看光谱
适用仪器
| 流式细胞仪 | |
| Ex: | 405 nm |
| Em: | 450/40 nm |
| 通道: | Pacific Blue 通道 |
样品实验方案
简要概述
- 用5×105至1×106细胞/ mL的密度制备含测试化合物的细胞
- 在0.5 mL细胞溶液中加入1 µL 500X Nuclear Violet
- 在室温下孵育30-60分钟
- 使用405nm紫色光激发流式细胞仪进行分析
实验步骤
1.对于每个样品,请在0.5 mL的温暖培养基或自备缓冲液中以5×105至1×106细胞/ mL的密度制备细胞。注意:应单独评估每种细胞系,以确定诱导凋亡的细胞密度。
2.用测试化合物处理细胞,以诱导凋亡或其他细胞周期功能。
3.向含有生长培养基的细胞中加入1µL 500X Nuclear Violet (组分A),并在37°C,5%CO2的培养箱中孵育细胞30至60分钟。注意:对于贴壁细胞,用0.5mM EDTA轻轻提起细胞以保持细胞完整,并在用Nuclear Violet 孵育之前用含血清的培养基洗涤一次。注意:适当的孵育时间取决于所用的单个细胞类型和细胞浓度。优化每个实验的孵育时间。注意:DNA染色前无需固定细胞,因为Nuclear Violet 具有细胞渗透性。
4.可选:以1000 rpm离心细胞4分钟,然后将细胞重悬于0.5 mL检测缓冲液(组分B)或自备缓冲液中。
5.使用405 nm紫色激光(Ex / Em = 405/445 nm)通过流式细胞仪检测荧光强度。
参考文献
Cell cycle synchronization of Escherichia coli using the stringent response, with fluorescence labeling assays for DNA content and replication
Authors: Ferullo DJ, Cooper DL, Moore HR, Lovett ST.
Journal: Methods (2009): 8
DNA replication, cell cycle progression and the targeted gene repair reaction
Authors: Engstrom JU, Kmiec EB.
Journal: Cell Cycle (2008): 1402
Morin inhibits the growth of human leukemia HL-60 cells via cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis through mitochondria dependent pathway
Authors: Kuo HM, Chang LS, Lin YL, Lu HF, Yang JS, Lee JH, Chung JG.
Journal: Anticancer Res (2007): 395
Direct control of cell cycle gene expression by proto-oncogene product ACTR, and its autoregulation underlies its transforming activity
Authors: Louie MC, Revenko AS, Zou JX, Yao J, Chen HW.
Journal: Mol Cell Biol (2006): 3810
Cell cycle markers for live cell analyses
Authors: Easwaran HP, Leonhardt H, Cardoso MC.
Journal: Cell Cycle (2005): 453
Dynamic relocalization of hOGG1 during the cell cycle is disrupted in cells harbouring the hOGG1-Cys326 polymorphic variant
Authors: Luna L, Rolseth V, Hildrestr and GA, Otterlei M, Dantzer F, Bjoras M, Seeberg E.
Journal: Nucleic Acids Res (2005): 1813
Dynamics of relative chromosome position during the cell cycle
Authors: Essers J, van Cappellen WA, Theil AF, van Drunen E, Jaspers NG, Hoeijmakers JH, Wyman C, Vermeulen W, Kanaar R.
Journal: Mol Biol Cell (2005): 769
Cell cycle regulation of the murine 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase (mOGG1): mOGG1 associates with microtubules during interphase and mitosis
Authors: Conlon KA, Zharkov DO, Berrios M.
Journal: DNA Repair (Amst) (2004): 1601
Description of a flow cytometry approach based on SYBR-14 staining for the assessment of DNA content, cell cycle analysis, and sorting of living normal and neoplastic cells
Authors: Nunez R, Garay N, Villafane C, Bruno A, Lindgren V.
Journal: Exp Mol Pathol (2004): 29
Differential roles of STAT1alpha and STAT1beta in fludarabine-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human B cells
Authors: Baran-Marszak F, Feuillard J, Najjar I, Le Clorennec C, Bechet JM, Dusanter-Fourt I, Bornkamm GW, Raphael M, Fagard R.
Journal: Blood (2004): 2475
