上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
Cell Meter 磷脂酰丝氨酸细胞凋亡检测试剂盒 蓝色荧光 405nm激发价格 2823
产品规格
产品货号
| Ex (nm) | – | Em (nm) | – |
| 分子量 | – | 溶剂 | – |
| 存储条件 | – |
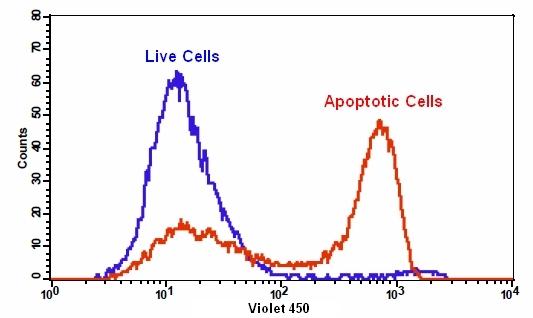
我们的Cell Meter 检测试剂盒是一套用于检测细胞生存力的工具。有多种参数可用于监测细胞活力。该特定试剂盒旨在通过测量磷脂酰丝氨酸(PS)的转运来检测细胞凋亡。在细胞凋亡中,PS转移到质膜的外部小叶。磷脂酰丝氨酸在细胞表面的出现是细胞凋亡初始/中间阶段的普遍指标,可以在观察形态变化之前进行检测。该试剂盒中使用的我们专有的Apopxin PS指示剂是基于小分子的PS指示剂。 PS指示剂与膜PS结合后具有蓝色荧光。试剂盒中使用的PS染料具有与PacificBlue®(PacificBlue®是Invitrogen的商标)相似的光谱特性。蓝色荧光染料在405nm处被紫色激发光充分激发,并在〜450 nm处发出强烈的蓝色荧光。该试剂盒经过优化,可与配备了紫色激发光的流式细胞仪一起使用。它特别适用于细胞的多色流式细胞术分析。金畔生物是AAT Bioquest的中国代理商,为您提供优质的Cell Meter 磷脂酰丝氨酸细胞凋亡检测试剂盒。
适用仪器
| 流式细胞仪 | |
| Ex: | 405 nm |
| Em: | 450/40 nm |
| 通道: | Pacific Blue 通道 |
|
荧光显微镜 |
|
| Ex: | Violet 滤波片组 |
| Em: | Violet 滤波片组 |
| 推荐孔板: | 黑色透明底板 |
样品实验方案
简要概述
- 用测试化合物制备细胞(200 µL /样品)
- 添加Apopxin 紫色450分析溶液
- 在室温下孵育30至60分钟
- 使用带有450/40 nm滤光片(Pacific Blue通道)的流式细胞仪或带有紫色滤光片的荧光显微镜分析细胞
实验步骤
1.用Apopxin 紫色450准备和孵育细胞:
1.1用测试化合物处理细胞一段时间(对于用星形孢菌素处理过的Jurkat细胞,需要4-6小时)以诱导细胞凋亡。
1.2离心细胞以获得1-5×105细胞/管。
1.3将细胞重悬于200 µL分析缓冲液(组分B)中。
1.4向细胞中加入2 µL Apopxin 紫色450(组分A)。
1.5可选:向坏死细胞中加入2 µL 100X碘化丙啶(组分C)。
1.6避光保存,于室温下孵育30至60分钟。
1.7在使用流式细胞仪或荧光显微镜分析细胞之前,添加300 µL分析缓冲液(组分B)以增加体积。
1.8使用带有450/40 nm滤光片的流式细胞仪(Pacific Blue通道)或带有紫色滤光片的荧光显微镜检测荧光强度。
2.通过使用流式细胞仪进行分析:
2.1使用带有450/40 nm滤光片(Pacific Blue通道)的流式细胞仪定量Apopxin Violet 450结合物。 将碘化丙锭加入细胞后,使用610/20 nm滤光片(PE-Texas Red通道)测量细胞活力。 注意:由于对细胞的分离或收获过程中可能会发生特定的膜损伤,因此不对贴壁细胞的Apopxin 结合流式细胞术进行常规测试。
3.通过使用荧光显微镜进行分析:
3.1孵育后用移液管吸移细胞悬液,用测定缓冲液冲洗1-2次,然后用测定缓冲液重悬细胞。
3.2将细胞添加到载玻片上。 注意:对于贴壁细胞,建议直接在盖玻片上生长细胞。 与Apopxin Violet 450孵育后,用Assay Buffer冲洗1-2次,然后将Assay Buffer加到盖玻片上。 将玻片上的盖玻片倒置并可视化细胞。 与Apopxin Violet 450孵育后,还可以将细胞固定在2%甲醛中,并在显微镜下观察。
3.3在带有紫色滤光片的荧光显微镜下,用Apopxin 紫色450分析凋亡细胞。 当碘化丙啶添加到细胞中时,使用TRITC滤波片检测细胞活力。 质膜上的蓝色染色表明Apopxin Violet 450与细胞表面的PS结合。
参考文献
Apoptosis of human Burkitt’s lymphoma cells induced by 2-N,N-diethylaminocarbonyloxymethyl-1-diphenylmethyl-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxybe nzoyl) piperazine hydrochloride (PMS-1077)
Authors: Wang WD, Xu XM, Chen Y, Jiang P, Dong CZ, Wang Q.
Journal: Arch Pharm Res (2009): 1727
Detection of apoptosis based on the interaction between annexin V and phosphatidylserine
Authors: Liu T, Zhu W, Yang X, Chen L, Yang R, Hua Z, Li G.
Journal: Anal Chem (2009): 2410
Dynamic analysis of apoptosis using cyanine SYTO probes: from classical to microfluidic cytometry
Authors: Wlodkowic D, Skommer J, Faley S, Darzynkiewicz Z, Cooper JM.
Journal: Exp Cell Res (2009): 1706
Eurycomanone induce apoptosis in HepG2 cells via up-regulation of p53
Authors: Zakaria Y, Rahmat A, Pihie AH, Abdullah NR, Houghton PJ.
Journal: Cancer Cell Int (2009): 16
Evaluation of cell surface expression of phosphatidylserine in ovarian carcinoma effusions using the annexin-V/7-AAD assay: clinical relevance and comparison with other apoptosis parameters
Authors: Dong HP, Holth A, Kleinberg L, Ruud MG, Elstr and MB, Trope CG, Davidson B, Risberg B.
Journal: Am J Clin Pathol (2009): 756
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 and Omi/HtrA2 induce annexin A2 cleavage followed by cell cycle inhibition and apoptosis
Authors: Wang CY, Lin YS, Su WC, Chen CL, Lin CF.
Journal: Mol Biol Cell (2009): 4153
Gold fluorescent annexin A5 as a novel apoptosis detection tool
Authors: Kurschus FC, Pal PP, Baumler P, Jenne DE, Wiltschi B, Budisa N.
Journal: Cytometry A (2009): 626
Induction of apoptosis in sonoporation and ultrasonic gene transfer
Authors: Miller DL, Dou C.
Journal: Ultrasound Med Biol (2009): 144
Mobilization of lysosomal calcium regulates the externalization of phosphatidylserine during apoptosis
Authors: Mirnikjoo B, Balasubramanian K, Schroit AJ.
Journal: J Biol Chem (2009): 6918
Peptidic targeting of phosphatidylserine for the MRI detection of apoptosis in atherosclerotic plaques
Authors: Burtea C, Laurent S, Lancelot E, Ballet S, Murariu O, Rousseaux O, Port M, V and er Elst L, Corot C, Muller RN.
Journal: Mol Pharm (2009): 1903
