上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
Cell Meter 线粒体膜电位检测试剂盒 红色荧光 适合流式细胞检测 价格 2823
产品规格
产品货号
| Ex (nm) | 613 | Em (nm) | 631 |
| 分子量 | – | 溶剂 | – |
| 存储条件 | – |
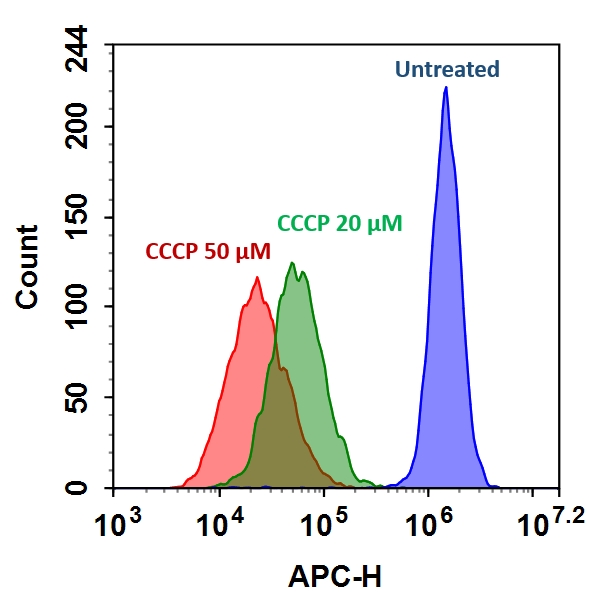
我们的Cell Meter 检测试剂盒是一套用于检测细胞功能的工具。可以使用多种参数。该特定试剂盒旨在通过测量线粒体膜电位(MMP)的丢失来检测细胞凋亡。线粒体膜电位的凋亡与线粒体通透性过渡孔的开放相吻合,导致细胞色素C释放到细胞质中,进而触发凋亡级联反应中的其他下游事件。该荧光测定法使用我们专有的阳离子MitoLite red检测细胞中线粒体膜电位的变化。在正常细胞中,当线粒体中积累了MitoLite red时,红色荧光强度会增加。但是,在凋亡细胞中,MMP凋亡后,MitoLite red的荧光强度降低。可以对用MitoLite red染色的细胞进行荧光检测。我们的Cell Meter 红色线粒体膜电位测定试剂盒可通过优化的测定方法提供所有必需成分。该试剂盒可用于筛选凋亡抑制剂。该试剂盒可以使用流式细胞仪在APC或Cy5通道上观察用MitoTell Red染色的细胞。该试剂盒经过优化,可通过流式细胞仪筛选凋亡抑制剂。金畔生物是AAT Bioquest的中国代理商,为您提供优质的Cell Meter 线粒体膜电位检测试剂盒。
点击查看光谱
适用仪器
| 流式细胞仪 | |
| Ex: | 640 nm |
| Em: | 660/20 nm |
| 通道: | APC 通道 |
样品实验方案
简要概述
- 用5×105至1×106细胞/ mL的密度制备含测试化合物的细胞
- 在0.5 mL细胞溶液中加入1 µL 500X MitoTell Red
- 将细胞在37°C,5%CO2培养箱中孵育15-30分钟
- 沉淀细胞,然后将细胞重悬于0.5 mL检测缓冲液中
- 使用带有APC或Cy5通道的流式细胞仪分析细胞
实验步骤
1.对于每个样品,在0.5 mL温暖的培养基或自备的缓冲液中以5×105至1×106细胞/ mL的密度制备细胞。注意:应单独评估每种细胞系,以确定诱导凋亡的细胞密度。
2.用测试化合物处理细胞一段时间,以诱导细胞凋亡,并建立平行对照实验。注意:我们在37ºC下用20µM CCCP处理Jurkat细胞15分钟,以改变线粒体膜电位。CCCP或FCCP可以与MitoTell Red同时添加。为了获得结果,可能需要为每个单独的细胞系滴定CCCP或FCCP。
3.向处理过的细胞中加入1 µL 500X MitoTell Red(组分A)。
4.将细胞在37°C,5%CO2培养箱中孵育15至30分钟。注意:对于贴壁细胞,用0.5 mM EDTA轻轻提起细胞以保持细胞完整,并在与MitoTell Red孵育之前用含血清的培养基洗涤细胞一次。
5.以800 rpm的速度离心细胞4分钟,然后将细胞重悬于0.5 mL的测定缓冲液(组分B)或自备的缓冲液中。
6.使用流式细胞仪通过APC或Cy5通道检测荧光强度。
参考文献
Safranine O as a fluorescent probe for mitochondrial membrane potential studied on the single particle level and in suspension
Authors: Perevoshchikova IV, Sorochkina AI, Zorov DB, Antonenko YN.
Journal: Biochemistry (Mosc) (2009): 663
Computer-assisted live cell analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential, morphology and calcium handling
Authors: Koopman WJ, Distelmaier F, Esseling JJ, Smeitink JA, Willems PH.
Journal: Methods (2008): 304
Determination of high mitochondrial membrane potential in spermatozoa loaded with the mitochondrial probe 5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethylbenzimidazolyl-carbocyanine iodide (JC-1) by using fluorescence-activated flow cytometry
Authors: Guthrie HD, Welch GR.
Journal: Methods Mol Biol (2008): 89
Effects of eprosartan on mitochondrial membrane potential and H2O2 levels in leucocytes in hypertension
Authors: Labios M, Martinez M, Gabriel F, Guiral V, Ruiz-Aja S, Beltran B, Munoz A.
Journal: J Hum Hypertens (2008): 493
Evaluation of sperm mitochondrial membrane potential by JC-1 fluorescent staining and flow cytometry
Authors: Xia XY, Wu YM, Hou BS, Yang B, Pan LJ, Shi YC, Jin BF, Shao Y, Cui YX, Huang YF.
Journal: Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue (2008): 135
How DASPMI reveals mitochondrial membrane potential: fluorescence decay kinetics and steady-state anisotropy in living cells
Authors: Ramadass R, Bereiter-Hahn J.
Journal: Biophys J (2008): 4068
Life cell quantification of mitochondrial membrane potential at the single organelle level
Authors: Distelmaier F, Koopman WJ, Testa ER, de Jong AS, Swarts HG, Mayatepek E, Smeitink JA, Willems PH.
Journal: Cytometry A (2008): 129
Mitochondrial membrane potential in axons increases with local nerve growth factor or semaphorin signaling
Authors: Verburg J, Hollenbeck PJ.
Journal: J Neurosci (2008): 8306
The mitochondrial membrane potential and Ca2+ oscillations in smooth muscle
Authors: Chalmers S, McCarron JG.
Journal: J Cell Sci (2008): 75
Cyclosporin A-induced oxidative stress is not the consequence of an increase in mitochondrial membrane potential
Authors: van der Toorn M, Kauffman HF, van der Deen M, Slebos DJ, Koeter GH, Gans RO, Bakker SJ.
Journal: Febs J (2007): 3003
