上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
Cell Meter 线粒体膜电位近红外检测试剂盒 适合微孔板检测 价格 2823
产品规格
产品货号
| Ex (nm) | – | Em (nm) | – |
| 分子量 | – | 溶剂 | – |
| 存储条件 | 在零下15度以下保存, 避免光照 |
我们的Cell Meter 检测试剂盒是一套用于检测细胞生存力的工具。有多种参数可用于检测细胞活力。该特定试剂盒旨在通过测量线粒体膜电位的丧失来监测细胞凋亡。线粒体膜电位的崩溃与线粒体通透性过渡孔的开放相吻合,导致细胞色素C释放到细胞质中,进而触发凋亡级联反应中的其他下游事件。我们的Cell Meter NIR线粒体膜电位检测试剂盒为所有必需成分提供了优化的测定方法,可检测线粒体膜电位丧失的细胞凋亡。该荧光测定法是基于我们专有的阳离子MitoLite NIR 染料对细胞中线粒体膜电位的检测。在正常细胞中,MitoLite NIR 主要在线粒体中积累,但是在凋亡细胞中,MitoLite NIR 染色强度降低。用MitoLite NIR 染色的细胞可以在620-640 nm激发下在660-680 nm荧光下进行检测。该试剂盒可用于筛选凋亡和抑制剂。该测定可以以方便的96孔和384孔荧光微量滴定板形式进行。金畔生物是AAT Bioquest的中国代理商,为您提供优质的Cell Meter 线粒体膜电位近红外检测试剂盒。
点击查看光谱
荧光酶标仪 |
|
| Ex: | 640 nm |
| Em: | 680 nm |
| Cutoff: | 665 nm |
| 推荐孔板: | 黑色透明底板 |
| 读取模式: | 底读模式 |
样品实验方案
简要概述
- 准备细胞
- 添加测试化合物
- 添加MitoLite NIR工作溶液(100 µL /孔/ 96孔板或25 µL /孔/ 384孔板)
- 在5%CO2的培养箱中于37°C孵育30-60分钟
- 添加测定缓冲液B(50 µL /孔/ 96孔板或12.5 µL /孔/ 384孔板)
- 检测Ex / Em = 640/680 nm(截止= 665 nm)的荧光强度(底部读取模式)
溶液配制
工作溶液配制
将50 µL的200X MitoLite NIR(组分A)添加到10 mL的测定缓冲液A(组分B)中,并充分混合以制成MitoLite NIR工作溶液,避光。
操作步骤
1.用测试化合物处理细胞一段所需的时间,以诱导细胞凋亡并建立平行对照实验。
阴性对照:仅用载体处理细胞。
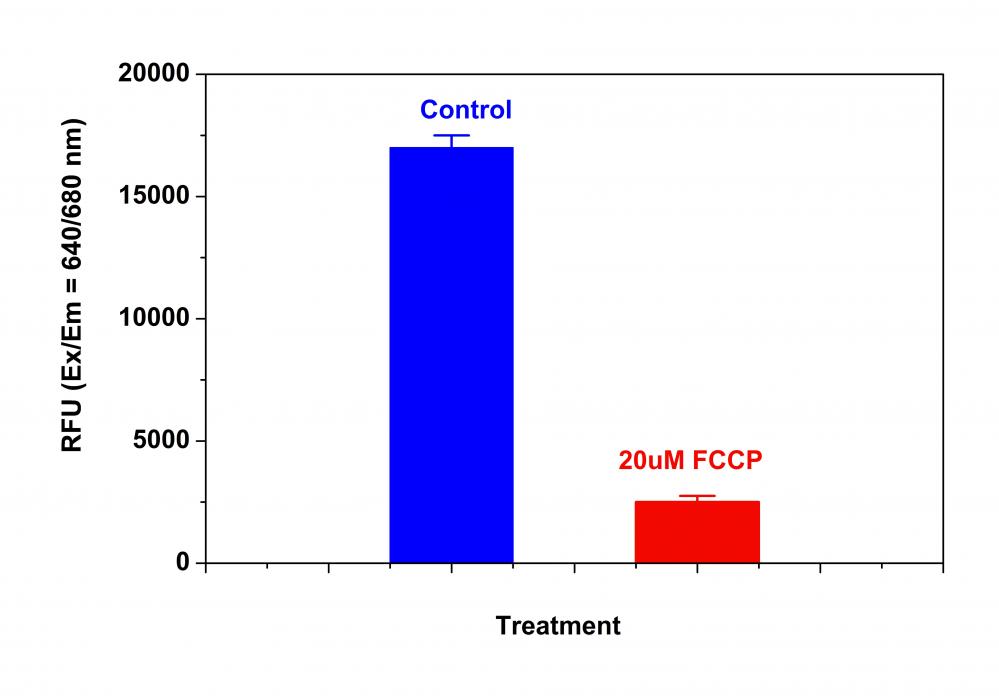
阳性对照:在37℃,5%CO2培养箱中,以5-50 µM的浓度用FCCP或CCCP处理细胞15至30分钟。 注意:CCCP或FCCP可以与MitoLite NIR同时添加。 为了获得结果,可能需要为每个单独的细胞系滴定CCCP或FCCP。
2.在添加MitoLite NIR工作溶液之前,请去除细胞培养基。注意:在添加MitoLite NIR工作溶液之前,必须除去细胞培养基。
3.将100 µL /孔/ 96孔板或25 µL /孔/ 384孔板的MitoLite NIR工作溶液添加到细胞板中。
4.在37°C,5%CO2的培养箱中避光放置30-60分钟。注意:适当的孵育时间取决于所用的单个细胞类型和细胞浓度。优化每个实验的孵育时间。
5.在检测荧光信号之前,将50 µL /孔/ 96孔板或12.5 µL /孔/ 384孔板的测定缓冲液B(组分C)加入细胞板。注意:加载后请勿洗涤细胞。对于非贴壁细胞,建议在加入测定缓冲液B(组分C)后,以800 rpm离心细胞板2分钟,然后制动。
6.加入测定缓冲液B(组分)10到30分钟后,使用荧光酶标仪(底部读取模式)(Ex / Em = 640/680 nm(Cutoff = 665 nm))检测荧光强度。
参考文献
Safranine O as a fluorescent probe for mitochondrial membrane potential studied on the single particle level and in suspension
Authors: Perevoshchikova IV, Sorochkina AI, Zorov DB, Antonenko YN.
Journal: Biochemistry (Mosc) (2009): 663
Computer-assisted live cell analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential, morphology and calcium handling
Authors: Koopman WJ, Distelmaier F, Esseling JJ, Smeitink JA, Willems PH.
Journal: Methods (2008): 304
Determination of high mitochondrial membrane potential in spermatozoa loaded with the mitochondrial probe 5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethylbenzimidazolyl-carbocyanine iodide (JC-1) by using fluorescence-activated flow cytometry
Authors: Guthrie HD, Welch GR.
Journal: Methods Mol Biol (2008): 89
Effects of eprosartan on mitochondrial membrane potential and H2O2 levels in leucocytes in hypertension
Authors: Labios M, Martinez M, Gabriel F, Guiral V, Ruiz-Aja S, Beltran B, Munoz A.
Journal: J Hum Hypertens (2008): 493
Evaluation of sperm mitochondrial membrane potential by JC-1 fluorescent staining and flow cytometry
Authors: Xia XY, Wu YM, Hou BS, Yang B, Pan LJ, Shi YC, Jin BF, Shao Y, Cui YX, Huang YF.
Journal: Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue (2008): 135
How DASPMI reveals mitochondrial membrane potential: fluorescence decay kinetics and steady-state anisotropy in living cells
Authors: Ramadass R, Bereiter-Hahn J.
Journal: Biophys J (2008): 4068
Life cell quantification of mitochondrial membrane potential at the single organelle level
Authors: Distelmaier F, Koopman WJ, Testa ER, de Jong AS, Swarts HG, Mayatepek E, Smeitink JA, Willems PH.
Journal: Cytometry A (2008): 129
Mitochondrial membrane potential in axons increases with local nerve growth factor or semaphorin signaling
Authors: Verburg J, Hollenbeck PJ.
Journal: J Neurosci (2008): 8306
The mitochondrial membrane potential and Ca2+ oscillations in smooth muscle
Authors: Chalmers S, McCarron JG.
Journal: J Cell Sci (2008): 75
Cyclosporin A-induced oxidative stress is not the consequence of an increase in mitochondrial membrane potential
Authors: van der Toorn M, Kauffman HF, van der Deen M, Slebos DJ, Koeter GH, Gans RO, Bakker SJ.
Journal: Febs J (2007): 3003
