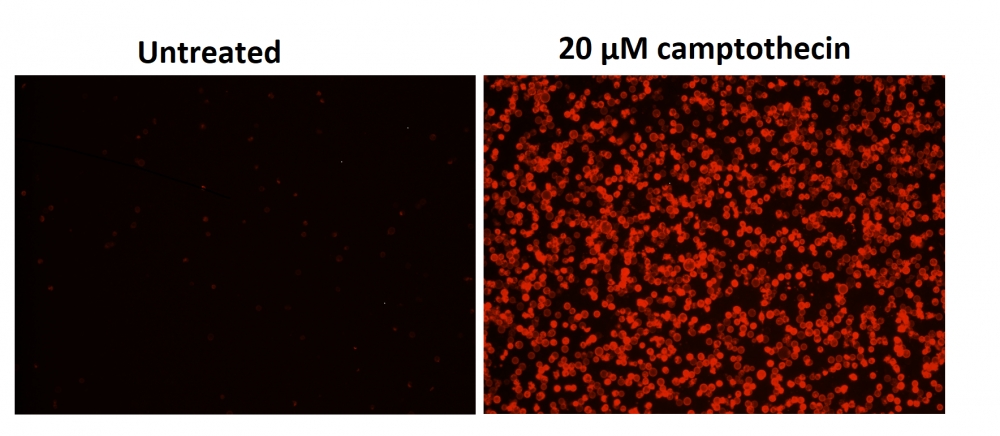
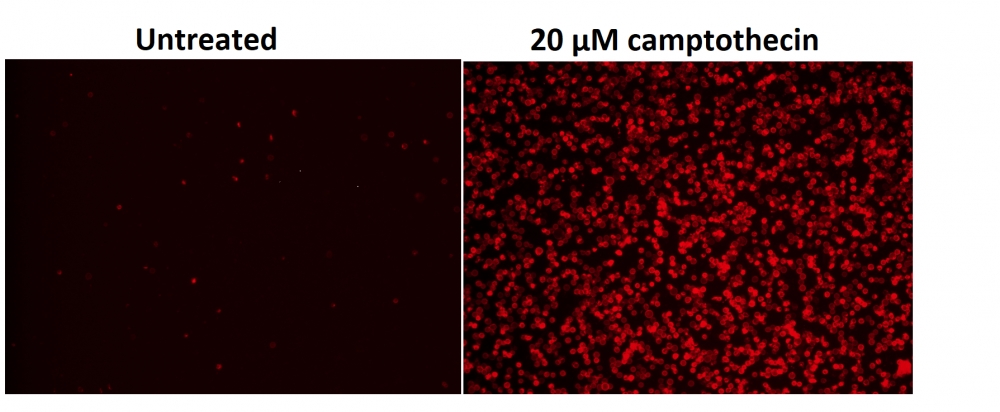
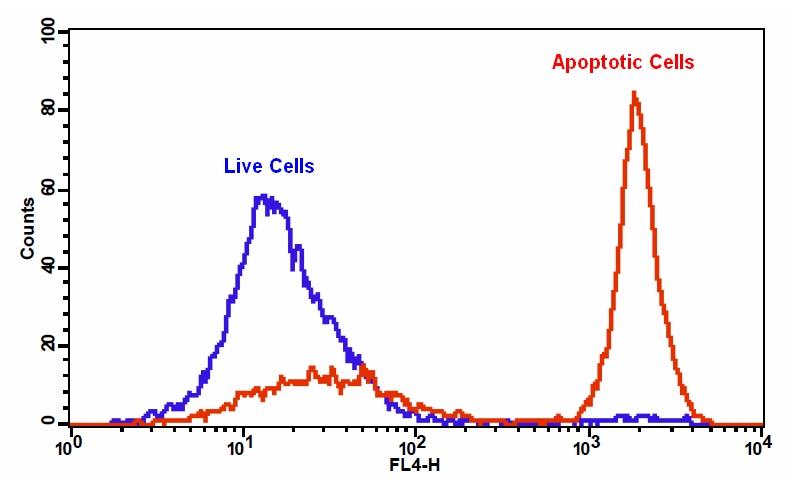
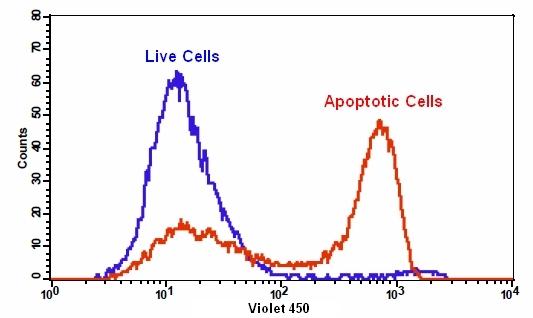
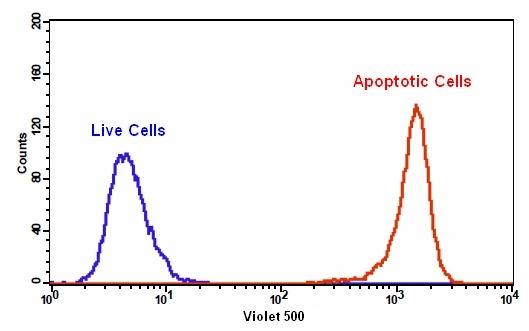
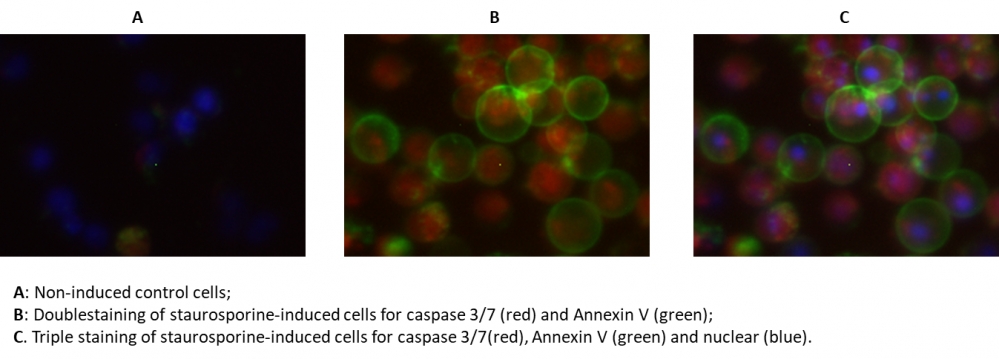
样品实验方案
简要概述
- 用2×106细胞/ mL的密度制备含测试化合物的细胞
- 以1:150的比例添加TF3-DEVD-FMK和/或Annexin V-iFluor 488,以1:100的比例添加到细胞溶液中
- 将细胞在37°C,5%CO2培养箱中孵育1小时。
- 沉淀细胞,用缓冲液或生长培养基洗涤并重悬细胞
- 使用带有FITC和TRITC滤光片的荧光显微镜或带有FL1的流式细胞仪和膜联蛋白V-iFluor 488 和TF3-DEVD-FMK的FL2通道,检测Ex / Em = 490/525 nm(截止= 515 nm)或550/595 nm(截止= 570 nm)的荧光强度(底部读取模式)。
溶液配制
储备溶液配制
1. TF3-DEVD-FMK储备溶液(150X):将200 µL DMSO加入小瓶TF3-DEVD-FMK(组分A)中,制成150X TF3-DEVD-FMK储备液。
实验步骤
1.根据您的特定诱导方案,将细胞培养至最适合凋亡诱导的密度,但在96孔板上不超过2 x 106细胞/ mL(或不超过3 x 105细胞/ 100 µL /孔) )。 同时,在每种标记条件下,用诱导群体相同的密度培养非诱导阴性对照细胞群体。 以下是在悬浮培养中诱导细胞凋亡的一些例子:
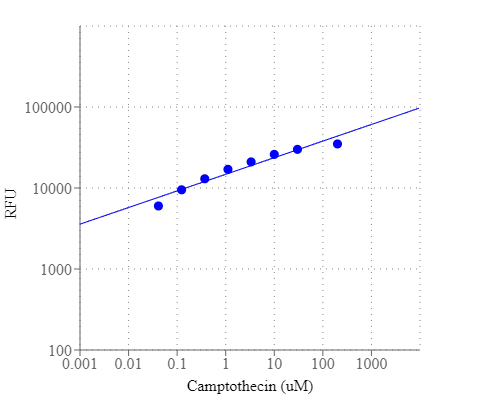
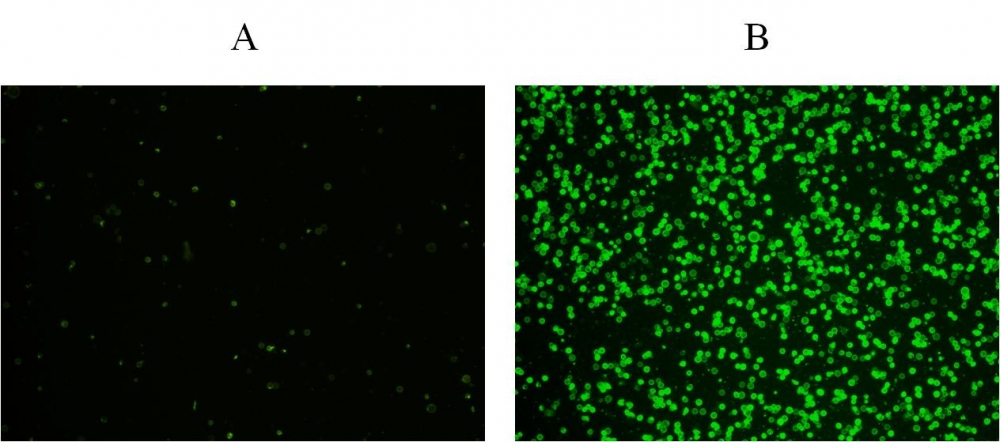
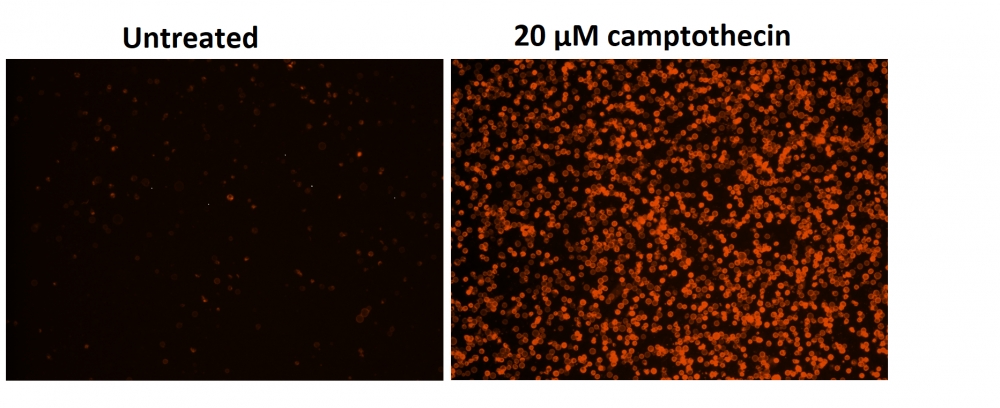
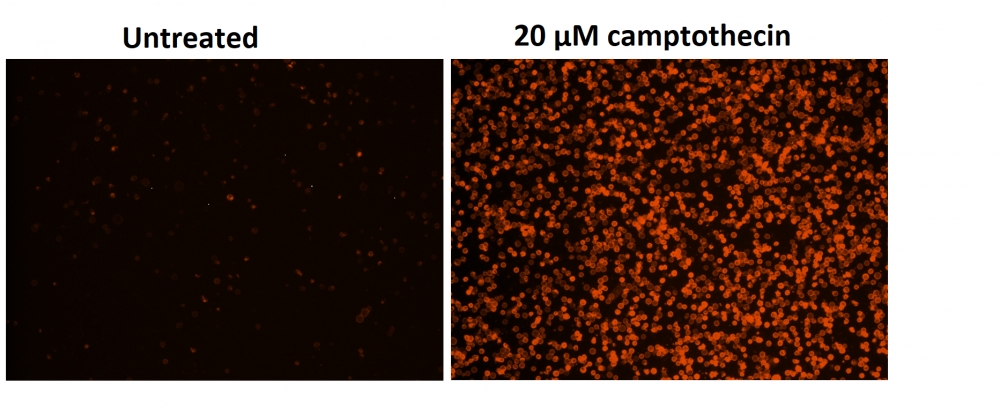
a.用2 µg / ml喜树碱处理Jurkat细胞3小时。
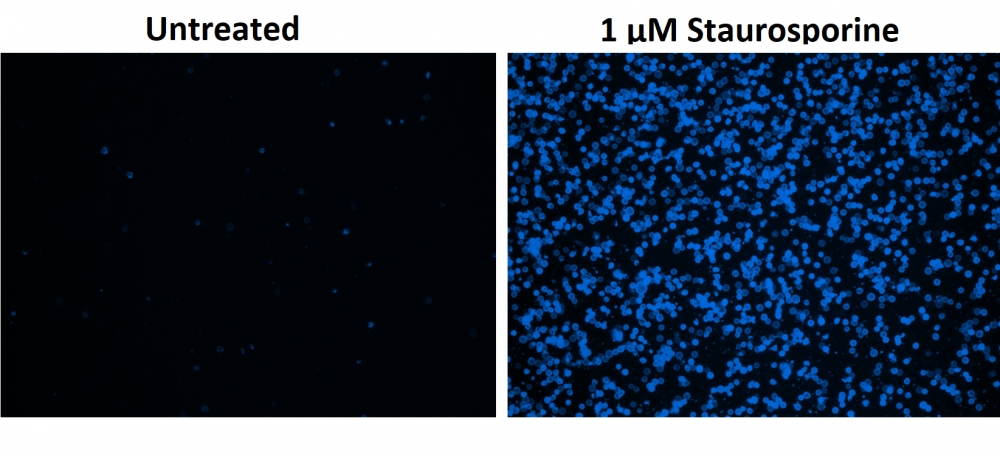
b.用1 µM星形孢菌素处理Jurkat细胞3小时。
c.用4 µg / ml喜树碱处理HL-60细胞4小时。
d.用1 µM星形孢菌素处理HL-60细胞4小时。 注意:应单独评估每种细胞系,以确定诱导凋亡的细胞密度。
2.以1:150的比例添加150X TF3-DEVD-FMK储备溶液和或以1:100的比例将Annexin V-iFluor 488 (组分B)添加到每个孔中。
3.将细胞在37°C,5%CO2培养箱中孵育1小时。 注意:对于TF3-DEVD-FMK标记,细胞可以浓缩至约5 X 106细胞/ mL。 对于贴壁细胞,用0.5 mM EDTA轻轻提起细胞以保持细胞完整,并在与TF3-DEVD-FMK孵育之前用含血清的培养基洗涤一次。 合适的孵育时间取决于所用的单个细胞类型和细胞浓度。 优化每个实验的孵育时间。 贴壁细胞的膜联蛋白V流式细胞仪分析未经过常规测试,因为在细胞分离或收获过程中可能会发生特定的膜损伤。
4.如果需要,用DNA染色剂标记细胞(例如,对于整个细胞核染色剂,使用Hoechst标记,或者如果仅用Annexin V-iFluor 488 标记细胞,则用碘化丙啶标记死细胞)。
5.以约200g的转速旋转细胞2分钟,并用1 mL(或使用96孔板的孔,每孔200 µL)洗涤细胞(组分E)洗涤两次。 用所需量的洗涤缓冲液重悬细胞。 注意:TF3-DEVD-FMK和Annexin V-iFluor 488 是荧光的,因此重要的是洗净任何未结合的试剂以消除背景。 对于分离的细胞,应将细胞浓度调整为每个酶标仪孔,2-5 X 105细胞/ 100 µL等分试样。
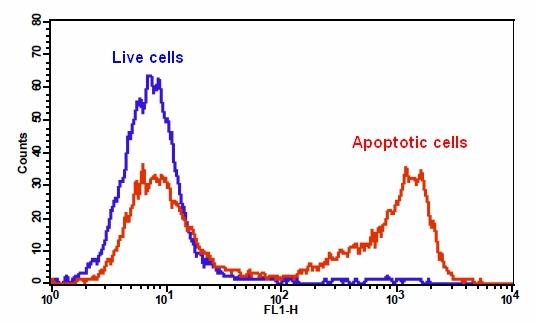
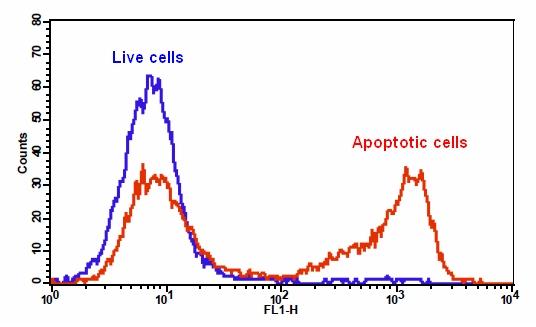
6.通过荧光显微镜,流式细胞仪或荧光酶标仪检测荧光强度,对于TF3-DEVD-FMK,Ex / Em = 550/595 nm;对于Annexin V-iFluor 488 ,490/525;对于Hoechst染色,350/461 nm;碘化丙锭为535/635。
对于流式细胞仪:使用膜联蛋白V-iFluor 488 的FL1通道,用于TF3-DEVD-FMK的FL2通道来检测荧光强度。
对于荧光显微镜:将100 µL细胞悬液放入黑色96孔板的每个孔中。 在荧光显微镜下观察细胞,使用TRITC通道用于TF3-DEVD-FMK,FITC通道用于Annexin V-iFluor 488 (TRITC通道用于碘化丙啶染色,DAPI通道用于Hoechst染色)。
对于荧光酶标仪:将100 µL细胞悬液放入黑色96孔板的每个孔中。 使用荧光酶标仪在Ex / Em = 490/525 nm(截止= 515 nm)或550/595 nm(截止= 570 nn)的Ex / Em = 490/525 nm(截止= 515 nm)处检测荧光强度(底部读取模式)适用于TF3-DEVD-FMK。注意:如果需要平衡细胞浓度,请调整诱导细胞的悬浮液体积,使其接近非诱导细胞的细胞密度。如果细胞治疗不会导致受刺激的细胞数量急剧减少,则此调整步骤是可选的。
参考文献
Anthocyanin-rich blackcurrant extract inhibits proliferation of the MCF10A healthy human breast epithelial cell line through induction of G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis
Authors: Nanashima, Naoki and Horie, Kayo and Chiba, Mitsuru and Nakano, Manabu and Maeda, Hayato and Nakamura, Toshiya
Journal: Molecular Medicine Reports (2017): 6134–6141
Clusterin signals via ApoER2/VLDLR and induces meiosis of male germ cells
Authors: Riaz, Muhammad Assad and Stammler, Angelika and Borgers, Mareike and Konrad, Lutz
Journal: American Journal of Translational Research (2017): 1266
Detecting Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Necrosis
Authors: Coleman, Jack and Liu, Rui and Wang, Kathy and Kumar, Arun
Journal: Apoptosis Methods in Toxicology (2016): 77–92
A pharmaceutical preparation of Salvia miltiorrhiza protects cardiac myocytes from tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis and reduces angiotensin II-stimulated collagen synthesis in fibroblasts
Authors: Ling S, Luo R, Dai A, Guo Z, Guo R, Komesaroff PA.
Journal: Phytomedicine (2009): 56
Agmatine protects cultured retinal ganglion cells from tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis
Authors: Hong S, Kim CY, Lee JE, Seong GJ.
Journal: Life Sci (2009): 28
Concurrent induction of necrosis, apoptosis, and autophagy in ischemic preconditioned human livers formerly treated by chemotherapy
Authors: Domart MC, Esposti DD, Sebagh M, Olaya N, Harper F, Pierron G, Franc B, Tanabe KK, Debuire B, Azoulay D, Brenner C, Lemoine A.
Journal: J Hepatol (2009): 881
Down-regulation of myeloid cell leukemia 1 by epigallocatechin-3-gallate sensitizes rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts to tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis
Authors: Ahmed S, Silverman MD, Marotte H, Kwan K, Matuszczak N, Koch AE.
Journal: Arthritis Rheum (2009): 1282
Exaggerated up-regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha-dependent apoptosis in the older mouse liver following reperfusion injury: targeting liver protective strategies to patient age
Authors: Selzner M, Selzner N, Chen L, Borozan I, Sun J, Xue-Zhong M, Zhang J, McGilvray ID.
Journal: Liver Transpl (2009): 1594
Increased apoptosis in HepG2.2.15 cells with hepatitis B virus expression by synergistic induction of interferon-gamma and tumour necrosis factor-alpha
Authors: Shi H, Guan SH.
Journal: Liver Int (2009): 349
Outside-to-inside signaling through transmembrane tumor necrosis factor reverses pathologic interleukin-1beta production and deficient apoptosis of rheumatoid arthritis monocytes
Authors: Meusch U, Rossol M, Baerwald C, Hauschildt S, Wagner U.
Journal: Arthritis Rheum (2009): 2612